L’activité physique et le glycogène sont intimement liés. En effet, la pratique de la musculation implique de réaliser des efforts intenses. Pour y parvenir, votre corps et vos muscles ont besoin d’énergie. C’est, par exemple, le cas lorsque vous enchaînez des séries de squat ou de développé couché.
Mais savez-vous comment votre organisme stocke cette énergie ? Et comment il la libère dès que vous en avez besoin durant les entraînements ? C’est précisément le rôle du glycogène.
Le glycogène, en bref :
- Le glycogène est une source d’énergie essentielle pour les muscles.
- Il est stocké dans le foie et les muscles sous forme de glucose.
- Pendant l’effort, le corps puise dans les réserves de glycogène.
- Une baisse du glycogène entraîne fatigue et baisse des performances.
- Après 90 minutes d’effort intense, les réserves sont presque vides.
- Les lipides prennent alors le relais comme source d’énergie.
- Une alimentation adaptée aide à optimiser les réserves de glycogène.
- Après l’effort, recharger en glucides accélère la récupération.
Sommaire
Qu’est-ce que le glycogène ?
Lorsque vous faites une activité sportive, vos muscles ont besoin d’énergie. Reliés entre eux par nos précieuses articulations, cette énergie mécanique leur permet d’effectuer les innombrables mouvements que permet le corps humain.
Ce carburant provient de l’alimentation. Il est apporté par les glucides (le glucose), les lipides (les acides gras) et les protides. C’est pour cela qu’il est important d’adopter une alimentation saine et variée au quotidien.
A contrario, une diète trop sucrée ou trop calorique peut causer une sensation de fatigue chronique et bien d’autres désagréments pour la santé.
Une fois stockée dans l’organisme, cette énergie chimique est transformée en énergie mécanique par les muscles, grâce à notre fameux glycogène.
Le glycogène est un glucide complexe que l’on retrouve aussi bien dans le foie que dans les muscles. Il s’agit en réalité d’une grosse molécule, composée elle-même de plus petites molécules de glucose.
Le glycogène a donc la capacité de stocker l’énergie non utilisée par l’organisme pour la réutiliser plus tard.
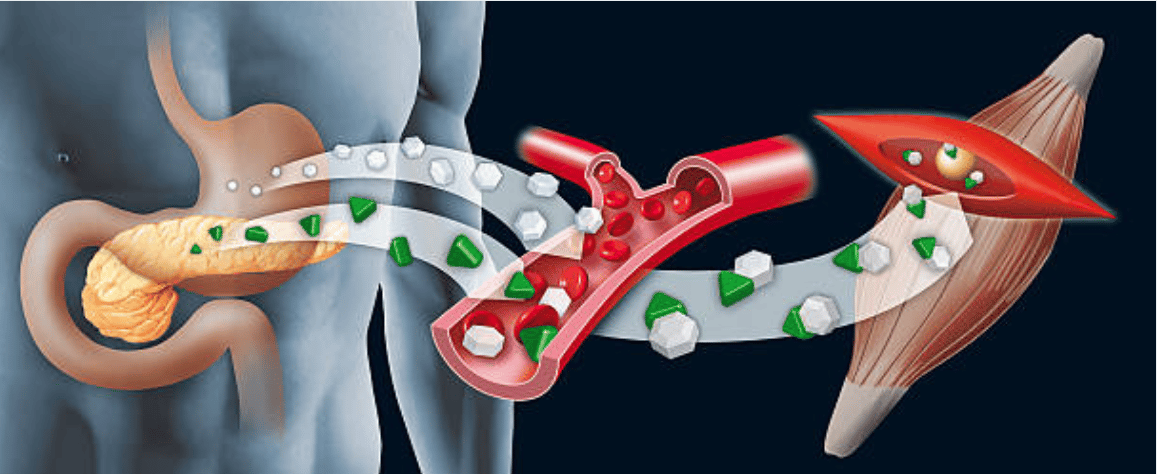
C’est exactement ce qu’il se passe lors d’un exercice physique. Lorsque les muscles ont besoin de glucose pour produire un effort, le corps pioche automatiquement dans les réserves de glycogène. Ce processus complexe porte le nom de glycogénolyse.
Dans toute pratique sportive, l’énergie est la source de la performance. Sans elle, vous serez contraint de ralentir ou de vous arrêter. Votre niveau de glycogène est donc essentiel. S’il est suffisant, tout se passe bien. Dans le cas contraire, vous n’aurez plus d’essence dans le moteur.
Que se passe-t-il lorsque les stocks de glycogène sont épuisés ?
Vos stocks de glycogène se vident et se remplissent au gré de vos efforts et de vos repas.
La dégradation du glycogène se fait de manière progressive. Elle est notamment conditionnée au niveau d’intensité et à la durée de l’activité.
Votre réserve de glycogène se videra après :
- 90 minutes d’activité sportive à 75 % de votre VO2 max (consommation maximale d’oxygène) ;
- Ou 4 heures d’activité sportive à 55 % de votre VO2 max.
Pour contrer cette carence en glycogène, une autre source d’énergie entre alors en scène et vous permet de récupérer de l’énergie : ce sont les lipides.
Les lipides sont les matières grasses contenues dans notre organisme et dans nos aliments. Contrairement aux idées reçues, ils constituent également des réserves d’énergie importantes pour notre organisme.
À intensité égale, un effort prolongé utilise un mélange de plus en plus riche en lipides et en acides aminés. Le muscle dégrade le glycogène du foie et les acides gras contenus dans le tissu adipeux. L’organisme fait quant à lui en sorte d’économiser son stock glycogénique. Le glycogène contenu dans les muscles sera ainsi converti en glucose.
Mais que se passe-t-il en cas d’épuisement total du niveau de glycogène ?
Une carence de cette source d’énergie est directement détectée par votre cerveau qui agit comme un interrupteur.

Celui-ci vous transmet un message d’arrêt de votre activité sportive. Vous ne pouvez plus continuer, car vous vous sentez trop fatigué et votre motivation disparaît. Les pratiquants de course à pied connaissent bien cette sensation. C’est un phénomène qui porte le nom de « mur du marathon ».
En résumé, l’épuisement du glycogène dans l’organisme contribue à baisser votre capacité à fournir un effort physique intense.
Attention toutefois à ne pas confondre cette fatigue induite par un manque d’énergie sous forme de glycogène avec la fatigue musculaire. Cette dernière peut intervenir lorsque vos muscles subissent des dommages lors de leur contraction, notamment pendant une séance de musculation très intense. Votre effort pourra également être stoppé de façon nette, même si votre volonté est toujours là, simplement parce que votre muscle ne peut absolument plus continuer.
Le rôle du glycogène pour les pratiquants de musculation
Maintenant que vous savez ce qu’est le glycogène, voyons comment vous pouvez vous en servir dans le cadre de votre pratique de la musculation pour favoriser l’hypertrophie.
Nous l’avons vu, la quantité de glucides consommée lors d’un effort dépend à la fois de son intensité et de sa durée. Le métabolisme des glucides sera sollicité lors d’une activité physique très intense. Au contraire, lors d’un exercice d’intensité plus faible, c’est le processus aérobie qui agit. Ce dernier sollicitera en priorité vos réserves de sucre, de graisses et de protéines.
Pour améliorer vos performances sportives, vous avez alors tout intérêt à augmenter vos stocks de glycogène. En effet, ce sont eux qui déterminent la durée pendant laquelle vous pourrez effectuer un effort intense. Pour ce faire, deux paramètres sont à prendre en compte : l’alimentation et l’entraînement.
Le régime alimentaire
Votre diète joue un rôle essentiel pour optimiser votre niveau de glycogène.
Avant une séance de musculation ou une épreuve sportive, veillez à soigner votre alimentation pour combler vos réserves énergétiques. En effet, l’état initial de vos stocks de glycogène est important.
Privilégiez des aliments qui ne perturberont pas votre digestion. Mais attention à l’index glycémique de chaque aliment !
Lors d’un entraînement, l’énergie est principalement apportée par le glycogène issu de vos repas quotidiens. Cet apport fournit de l’énergie pendant 60 à 90 minutes en fonction de votre stock de départ. Au-delà, votre réserve est épuisée et vos performances diminuent.
Pour compenser ce manque, vous aurez besoin d’un apport énergétique extérieur durant l’effort, qu’il s’agisse d’une boisson énergétique, d’une collation ou d’une barre de céréales. Vous pouvez opter aussi pour des aliments riches en glucides comme la banane, les fruits séchés ou les compotes.
Après l’effort, il est tout aussi capital de consommer des glucides, car ce sont des nutriments essentiels qui participent à la resynthèse en glycogène. Par conséquent, ils favorisent le développement de la masse musculaire et la récupération physique.
Cette période post-training de quelques heures durant laquelle vous devez assurer vos apports en glucides s’appelle la fenêtre anabolique.
| Phase de l’entraînement | Stratégies de gestion du glycogène | Aliments/Boissons recommandés |
|---|---|---|
| Avant l’effort | Maximiser les réserves | Aliments à faible indice glycémique, hydrates complexes |
| Pendant l’effort | Maintenir le niveau d’énergie | Boissons énergétiques, barres de céréales |
| Après l’effort | Reconstituer les réserves de glycogène | Glucides rapides (fruits, barres énergétiques), protéines |
Différents aliments peuvent vous aider à reconstituer vos stocks de glycogène :
- Les fruits et légumes, grâce à leur teneur en glucides
- Les produits laitiers, car ils contiennent des acides aminés essentiels
- Les aliments qui favorisent l’absorption de sucres rapides, comme du miel ou des barres énergétiques
- Les sucres lents, riches en amidon et en fécule
- Les oléagineux (amandes, noisettes, noix de cajou, pistaches, etc.), riches en protéines végétales
- Les flocons d’avoine
Vous avez également la possibilité de préparer une boisson protéinée à base de whey protein et de maltodextrine, une poudre composée de glucides issus du maïs, du blé, de la pomme de terre ou du riz.
Plus largement, une alimentation équilibrée est un facteur majeur pour une bonne recharge glucidique.
L’entraînement sportif
La manière dont vous vous entraînez à la salle de sport conditionne aussi la quantité de glycogène que vous pouvez stocker.
Plus vous vous exercez, plus vous améliorez votre sensibilité à l’insuline. Vous pourrez ainsi augmenter vos réserves de glycogène et améliorer vos performances.

DÉCOUVREZ TOUS MES PROGRAMMES
Comment utiliser le glycogène pour les compétitions de bodybuilding ?
Vider les réserves de glycogène volontairement est une pratique bien connue des pratiquants de culturisme. C’est le principe du rebond glucidique.
Avant une compétition ou une séance photo, le rebond glucidique permet aux bodybuilders d’afficher un meilleur physique. Cette pratique est donc plutôt réservée à celles et ceux qui font de la compétition.
Un rebond glucidique s’effectue après une sèche.
En période de sèche, les athlètes cherchent à perdre du poids. Ils diminuent progressivement leurs apports en glucides dans leur alimentation (contrairement aux phases de prise de masse musculaire). C’est le prix à payer pour obtenir un corps sec et musclé lors du concours.
Le fait de réduire cette consommation de glucides entraîne mécaniquement une baisse du stock de glycogène. Visuellement, cela cause une dégradation de l’aspect physique. Les muscles sont moins volumineux, ce qui peut coûter de précieux points au moment du classement final.
Le rebond glucidique consiste justement à rehausser brutalement la quantité de glucides dans l’organisme quelques jours avant la compétition, en jouant sur le volume d’eau sous-cutanée. De cette manière, les muscles paraîtront temporairement plus imposants.
Mettre en place un rebond glucidique avant une compétition n’est pas chose aisée. C’est pourquoi je vous ai préparé un programme complet d’une semaine pour aborder votre concours dans les meilleures dispositions.

PROGRAMME TOTAL REBORN 40+
Le meilleur accompagnement pour devenir SEC et MUSCLÉ, maximiser votre Testostérone et atteindre le Meilleur Physique de votre Vie après 40 ans.
Conclusion
Bien comprendre comment fonctionne le glycogène dans l’organisme est un véritable atout pour les pratiquants de musculation et autres sportifs. Cette molécule est notre source de carburant principale. Et c’est précisément en augmentant votre stock de glycogène musculaire que vous parviendrez à accroître vos performances.
FAQ
Le glycogène est une forme de stockage du glucose dans le foie et les muscles. Il fournit l’énergie nécessaire aux efforts physiques.
Lors d’un effort intense, le corps dégrade le glycogène en glucose pour alimenter les muscles en énergie.
Un manque de glycogène entraîne une forte fatigue et une baisse de performance. Le corps utilise alors les lipides comme source d’énergie.
Les réserves s’épuisent après environ 90 minutes d’effort intense ou 4 heures d’activité modérée.
Consommer des glucides après l’effort permet de reconstituer les réserves et d’accélérer la récupération.
Les fruits, les céréales complètes, les légumineuses et les aliments riches en amidon sont les meilleures sources de glucides.
Adopter une alimentation riche en glucides et bien structurer ses entraînements améliore le stockage et l’utilisation du glycogène.






