L’élongation musculaire est une blessure courante chez les sportifs. Malheureusement, les pratiquants de musculation et de fitness sont aussi concernés. S’il s’agit d’un traumatisme plutôt bénin à première vue, il convient toutefois de le traiter rapidement pour ne pas laisser la situation empirer.
Découvrez tout ce que vous devez savoir pour soigner efficacement ce type de blessure.
Soigner une élongation, en bref :
- L’élongation musculaire est un étirement excessif des fibres musculaires sans lésion grave.
- Elle survient souvent lors d’un effort physique, principalement aux jambes.
- Les causes incluent le manque d’échauffement, la fatigue et une mauvaise hydratation.
- La douleur est vive mais disparaît au repos, sans hématome ni œdème.
- Il faut arrêter immédiatement l’effort et appliquer de la glace dès l’apparition de la douleur.
- Le repos, la kinésithérapie et la rééducation sont essentiels pour éviter les récidives.
Sommaire
Qu’est-ce qu’une élongation musculaire ?
Une élongation musculaire désigne une blessure causée par un étirement anormal et excessif des fibres, sans lésion importante. Dans certains cas, il arrive que certaines petites fibres musculaires puissent être déchirées, sans gravité.
Lorsqu’une quantité plus importante de fibres du muscle touché est rompue, il ne s’agit plus d’une élongation, mais bel et bien d’une déchirure (autrement connue sous le nom de claquage). L’élongation est donc le premier niveau de la blessure.
Je vous invite à consulter cet article pour en savoir plus sur les différentes blessures en musculation.
L’élongation musculaire intervient généralement lors d’un effort physique. Elle peut toucher la quasi-totalité des muscles du corps humain, des cuisses aux mollets, en passant par les fessiers, les ischio-jambiers, les adducteurs, les biceps ou encore les triceps. Chez les sportifs, ce sont malgré tout les membres inférieurs qui sont le plus souvent impactés.

Les causes d’une élongation musculaire sont aujourd’hui bien connues. Le manque d’échauffement avant la pratique d’une activité sportive est sans nul doute l’une des plus courantes.
Combinée à un effort trop important, la fatigue peut aussi être à l’origine de cette blessure douloureuse. Des mouvements brusques durant l’activité physique, des déséquilibres musculaires ou posturaux et un manque d’hydratation sont également des facteurs à prendre en compte. Nous y reviendrons à la fin de cet article.
Quels sont les symptômes de cette blessure ?
L’élongation se caractérise par l’apparition soudaine d’une douleur vive au moment de la pratique sportive. Elle est cependant moins aiguë que lors d’une déchirure musculaire, souvent comparée à « un coup de poignard » par les sportifs qui en sont victimes.
Cette douleur, plus intense que celle d’une contracture, a tendance à disparaître lorsque le groupe musculaire concerné est au repos. Elle est en revanche bien présente et perceptible lors de la palpation, ou lorsque le muscle se contracte.
Une élongation musculaire n’entraîne pas l’apparition d’un hématome ou d’un œdème (gonflement) sur la zone douloureuse. Malheureusement, la formation d’un hématome est la plupart du temps le signe d’une lésion musculaire plus grave (déchirure, voire rupture totale).
Le diagnostic d’une élongation peut être confirmé par l’examen clinique d’un professionnel de santé tel qu’un kiné ou un médecin. En cas de doute, ce dernier pourra vous prescrire une échographie pour s’assurer que le traumatisme n’est pas plus important.
Mais alors, que faire si vous avez les symptômes d’une élongation musculaire ?
Le traitement à suivre pour soigner une élongation musculaire
Au moment de la blessure
En cas de douleur brutale, la première chose à faire est d’arrêter tout de suite votre séance de sport. Poursuivre votre effort aura pour conséquence d’aggraver la blessure et d’allonger la durée de votre indisponibilité à venir.
Il convient également de ne pas s’étirer. En effet, les étirements pourraient amplifier les micro-lésions survenues au niveau des fibres.
L’application de glace est fortement recommandée dès l’apparition de la douleur. Posez une poche de glace sur le groupe musculaire lésé durant 15 à 20 minutes. En attendant de consulter un médecin, vous pouvez bien entendu prendre un antalgique comme le paracétamol pour soulager la douleur.

Dans les jours qui suivent le traumatisme
Soigner une élongation musculaire implique de continuer à appliquer du froid dans les premiers jours (3 à 4 fois). Cet aspect est fondamental pour réduire l’inflammation et accélérer la guérison.
Votre médecin vous indiquera la durée d’indisponibilité. Par ailleurs, il vous prescrira des anti-inflammatoires non stéroïdiens (AINS) pour limiter l’inflammation.
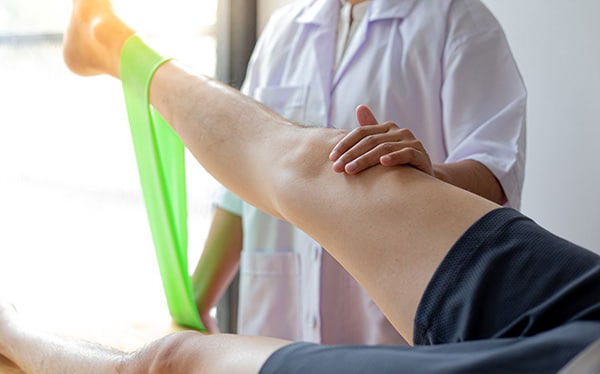
En outre, une bonne cicatrisation de la blessure passe par une phase de rééducation. Que vous soyez un sportif amateur ou un athlète de haut niveau, des séances de kinésithérapie sont essentielles pour renforcer et assouplir le muscle. Ce traitement vous aidera à prévenir les récidives.
Votre kinésithérapeute suivra un protocole bien défini. En plus des exercices de renforcement musculaire et de stretching, il pourra effectuer des massages et vous proposer des sessions d’électrostimulation et de cryothérapie.
La reprise du sport se fera progressivement après une dizaine de jours en moyenne. Elle est toutefois conditionnée à une disparition totale de la douleur musculaire.
Si vous étiez blessé à une jambe, vous devrez réaliser plusieurs sorties en footing de faible intensité avant de reprendre une activité cardio normale.
En cas de blessure au niveau du haut du corps, les premiers entraînements de musculation ne devront pas être trop brutaux. Privilégiez des charges faibles durant quelques séances pour ne pas rechuter.
Comment prévenir les élongations musculaires ?
Si vous pratiquez une activité physique telle que la musculation, vous devez accorder une importance toute particulière à la prévention des blessures. Plusieurs éléments doivent ainsi être pris en considération :
- L’échauffement
- L’hydratation
- L’alimentation
- La fatigue et le sommeil
- Le renforcement musculaire
- La souplesse
Votre échauffement
Pour éviter les blessures musculaires, il est avant tout indispensable de bien s’échauffer avant de faire du sport. 10 à 20 minutes d’échauffement permettront à votre corps de monter en température et à vos muscles et articulations d’effectuer les mouvements attendus en toute sécurité.
Vous ne savez pas comment faire ? Découvrez mes conseils de coach sportif pour bien vous échauffer avant une séance de musculation.
Votre hydratation et votre diète
Pendant l’effort, il est tout aussi important de bien vous hydrater pour compenser les pertes d’eau liées à la transpiration.
Plus largement, ce que vous mangez et ce que vous buvez au quotidien a des conséquences directes sur votre santé. Pour réduire le risque de blessure, adoptez une alimentation saine et équilibrée.
Le sommeil
Le sommeil et la récupération jouent un rôle majeur.
En cas de fatigue, il est préférable d’adapter l’intensité de vos entraînements en réduisant, par exemple, les charges utilisées ou le nombre de répétitions effectuées.
Le renforcement musculaire
Une faiblesse musculaire est souvent à l’origine de blessures à répétition. Par le biais de la musculation, un renforcement ciblé est le meilleur moyen de rattraper vos points faibles et de lutter contre ce phénomène.

DÉCOUVREZ MON COACHING PERSONNALISÉ
Sculptez le corps de vos rêves en moins de 90 jours.
Les assouplissements
Le fait de se blesser régulièrement peut enfin être causé par la raideur d’un muscle. Pour être performants, vos muscles ne doivent pas seulement être forts. Ils doivent aussi être souples pour résister aux contraintes imposées lors des entraînements.
Pensez à vous étirer plusieurs fois par semaine pour vous assouplir et ainsi limiter les accidents musculaires.
Conclusion
L’élongation musculaire est une blessure sans gravité si elle est prise immédiatement au sérieux. L’application de glace, le suivi de séances de kinésithérapie et quelques jours de repos suffiront pour vous en débarrasser.
Mais attention à ne pas négliger votre rééducation, sous peine de rechuter dès la reprise de votre activité physique.
FAQ
C’est un étirement excessif des fibres musculaires sans rupture importante. Elle provoque une douleur vive mais ne s’accompagne pas d’hématome.
Elle se manifeste par une douleur soudaine lors de l’effort, qui diminue au repos mais revient à la contraction du muscle.
L’élongation est un simple étirement des fibres, alors qu’une déchirure implique une rupture partielle du muscle et peut provoquer un hématome.
Arrêtez immédiatement l’effort, appliquez de la glace pendant 15 à 20 minutes et évitez les étirements. Consultez un professionnel si la douleur persiste.
La récupération prend généralement 7 à 10 jours, mais peut varier selon la gravité et les soins apportés.






